UCD COSMOgenic isotope Facility (UCIF)
Research facility specializing in the extraction of cosmogenic nuclides for geologic applications.
UCIF is a new cosmogenic isotope facility within the UCD School of Earth Science. The facility allows in-house preparation of rock samples through to generation of targets for accelerator mass spectrometry measurement, with applications in constraining earth surface processes.
The UCIF procedure is modified from that of UBuffalo, LDEO, and UVM. Rock samples are first crushed and sieved in the shared departmental crushing room, before they are moved to the UCIF Laboratory, where they undergo magnetic separation, density separation, acid etching and column chemistry procedures. The final prepared AMS target is then sent to an AMS facility for isotopic analysis.
Crushing Room:
The primary mechanical processing of rock samples takes place in the UCD Crushing Room, with the aid of a jaw crusher, disc mill and sieve shaker. In this step the solid rock samples are turned from chunks of rock up to tens of centimetres in length into sand which is then sieved to isolate the fraction with a grain size between 250 and 850 µm.
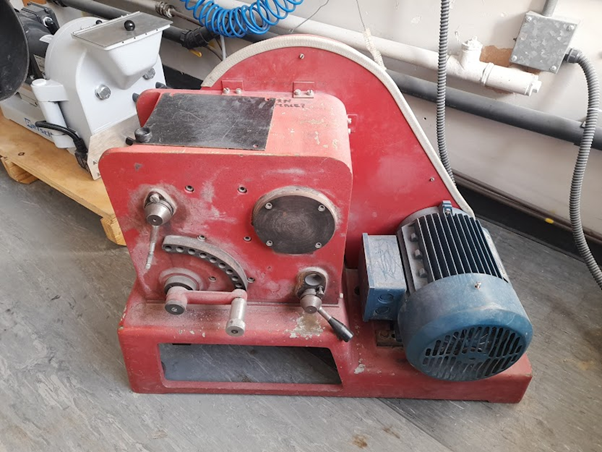
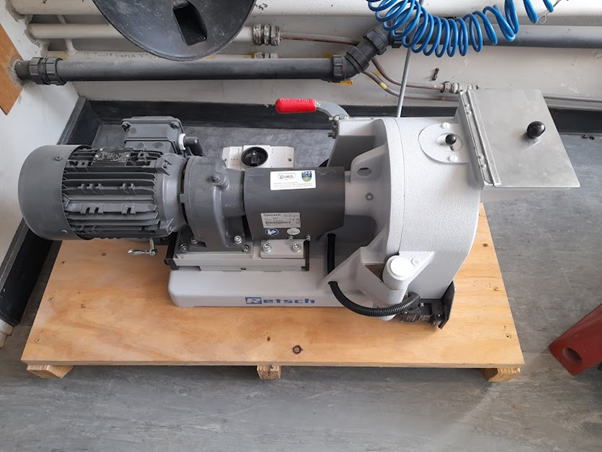
The Jaw Crusher
The Disc Mill
UCIF Laboratory:
On entering the lab, the 250-850 µm sample fraction goes through magnetic separation, whereby magnetic material is removed from the sample by passing a strong neodymium magnet over a thin layer of the sample. The magnetic fraction is then bagged separately and retained. In special circumstances a Franz magnetic separator is used.
Magnetic separation in progress
Next the magnetically clean sample undergoes several acid etching steps, first with HCl, and then twice with HF and HNO3.
Following initial acid cleaning steps, samples undergo a density separation using non-toxic lithium heteropolytungstate (LST) heavy liquid, which can be calibrated to have a density similar to that of quartz through the addition of water. This LST allows the quartz and other minerals with slightly different densities to be floated out from each other and then drained into separate pieces of filter paper. This step is highly effective at removing non-quartz material such as micas and feldspars.
Three seperate constituent parts of a processed granite sample floating in LST.
In progress…